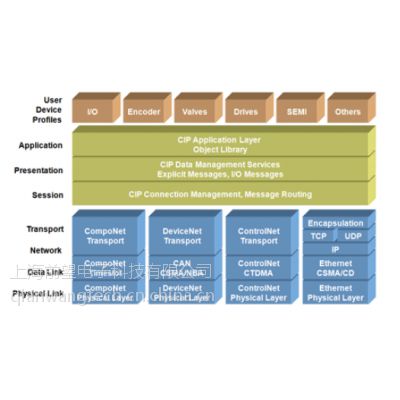
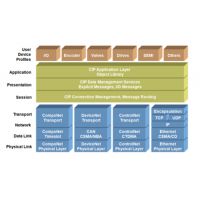
EtherNet/IP是四个开放式网络标准(CompoNet,DeviceNet, ControlNet和EtherNet / IP )之一,它们都使用一个相同的应用层, "通用工业协议"(CIP)。 这种通用的应用层和开源软件及硬件接口允许实现从控制层之上的现场总线级到企业级的自动化组件的通用连接。
CIP网络家族是由ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendor Association - )规定和发布的。
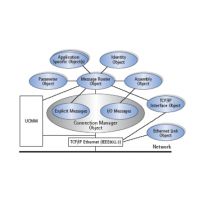
通用工业协议以对象模型的方式实现通信和应用。 预定义的对象方便了不同的设备和制造商之间的数据交换。 通过创建不同的设备配置文件,可以获取更多的用户利益。
CIP是一个基于连接的协议。 它定义了I/O数据交换,使用I/O报文(或隐式报文);以及使用显示报文的通用的数据交换,用于配置、诊断和管理。因此, CIP给用户提供了4个基本功能:
应用的通用对象模型
用于网络中数据交换的通用通信模型
通用的配置方法
通用的设备配置文件
EtherNet / IP是TCP / IP和以太网(IEEE 802.3)之上的CIP实现。
EtherNet / IP规范定义了第4层和第3层(传输层和网络层,使用封装协议和TCP / IP),以及第2层(数据链路层,使用以太网IEEE 802.3),层1和0(物理层和传输介质)。
连接器,电缆类型和电缆长度基于通信相关的显示、操作元件和封装相应的标签来***。
EtherNet/IP支持10 Mbit/s和100 Mbit/s的数据传输速率。 通常情况下,内置使用合适的(管理的)开关的星型拓扑结构,带有支持嵌入式开关的设备,也可以实现线性和环形拓扑结构。 连接到EtherNet/IP网络的设备的数量仅取决于可用的IP地址空间。
自2000年***推出以来,EtherNet / IP标准通过不断增加新功能获得提高,例如:
DLR(设备级环)协议
通过环形拓扑实现介质冗余QoS (服务质量)
基于IEEE 802.1D/Q和DSCP报文优化ACD (地址冲突检测)
检测并根据IP地址冲突行动CIP同步(使用IEEE 1588 PTP)
实现例如运动控制中的时间关键型应用
除了带I /O模块、阀门、编码器、驱动器和控制器(PLC)的工厂自动化外, EtherNet /IP的主要应用领域是控制和企业层的联网。在CIP网络家族内,EtherNet/ IP覆盖的应用场合包括网络中需要在平均周期时间(10ms到500ms及以上)内实现中等到大量的数据交换,以及在运动控制应用中所见的低于1ms的短周期时间内记录中等的数据量。
Introduction to EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP is one of four open network standards (CompoNet, DeviceNet, ControlNet and EtherNet/IP), which all use a common application layer, the "Common Industrial Protocol" (CIP). This common application layer and open software and hardware interfaces allow a universal connection of automation components from the fieldbus level over the control level to the enterprise level.
The Family of CIP Networks is specified and published by ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendor Association - 
The Common Industrial Protocol presents communication and application in the object model. Predefined objects facilitate the data exchange of different devices and manufacturers. By creating various device profiles, additional user benefits were achieved.
CIP is a connection based protocol. It defines the exchange of I/O data using I/O Messaging (or Implicit Messaging) as well as the exchange of general data for configuration, diagnostic and management via Explicit Messaging. CIP thus provides 4 essential functions to the user:
Common object model for application
Common communication model for data exchange in the network
Common configuration methods
Common device profiles
EtherNet/IP is the implementation of CIP over TCP/IP and Ethernet (IEEE 802.3).
The EtherNet/IP specification defines Layer 4 and Layer 3 (Transport and Network using Encapsulation Protocol and TCP/IP) as well as Layer 2 (Data Link, usage of Ethernet IEEE 802.3), Layers 1 and 0 (Physical Layer and Transmission Media).
Connectors, cable types and cable lengths are specified as are communication-based displays, operating elements and the corresponding labeling of the housing.
EtherNet/IP supports data rates of 10 Mbit/s and 100 Mbit/s. Normally, a star topology using suitable (managed) switches is built, with devices supporting embedded switches also line and ring topologies can be realised. The number of devices connected in an EtherNet/IP network depends only on the available IP-Address space.
Since its first introduction in 2000, the EtherNet/IP Standard continuesly has been enhanced by new features like:
DLR (Device Level Ring) Protocol
media redundancy by means of ring topologiesQoS (Quality of Services)
Priorisation of messages based on IEEE 802.1D/Q und DSCPACD (Address Conflict Detection)
detect and act upon IP address conflictsCIP Sync (uses IEEE 1588 PTP)
realisation of time critical applications like motion control
Besides factory automation with I/O-modules, valves, encoders, drives and controls (PLC), the main field of application of EtherNet/IP is the networking of both the control and the enterprise level. Within the Family of CIP Networks, EtherNet/IP covers applications where medium to large amount of data with medium cycle times (10 ms to 500 ms and above) need to be exchanged in the network as well as medium amount of data with short cycle times down to 1 ms as they are seen in motion control applications.